Factors Affecting Biomass Pyrolysis Products
Biomass Pyrolysis, is a process in which biomass feedstocks are decomposed into smaller molecules by heating in an anaerobic environment. The final products mainly include biochar, bio-oil, syngas, etc. The distribution and characteristics of these products are affected by the feedstock type, pyrolysis temperature, heating rate, residence time and other dimensions.
.jpg)
There are many types of biomass feedstocks, including wood, crop residues (e.g. straw, rice husk), livestock and poultry manure, energy crops, etc. Different types of biomass feedstocks differ in their chemical composition and pyrolysis properties, and therefore their final products will also differ.
Three main products are produced through biomass pyrolysis: bio-oil, bio-char and syngas. The proportion of output of these products depends largely on the composition of the biomass. For example, feedstocks with higher lignin content are more likely to produce biochar during the pyrolysis process, while feedstocks with higher cellulose and hemicellulose content are more likely to produce bio-oil and gas.
Low-temperature Pyrolysis : It mainly produces biochar, with less bio-oil and gas production.
Medium Temperature Pyrolysis: Bio-oil and gas production increases significantly, but biochar production remains high.
High-temperature Pyrolysis: Biochar production decreases further and bio-oil and gas production reaches a high level. Among them, high-temperature flash pyrolysis is mainly dominated by gas products.

Heating speed is also an important factor affecting the distribution of biomass pyrolysis products. The faster the heating speed, the shorter the residence time of biomass feedstock in the pyrolysis process, which is conducive to generating more liquid products (bio-oil) and gas products.
Slow pyrolysis: Slower heating rates allow longer pyrolysis reaction times, mainly for biochar production.
Fast pyrolysis: Conversely, the faster the heating rate, the shorter the reaction time for pyrolysis, mainly used for bio-oil production and gas product production.
Flash pyrolysis: With extremely fast heating rates, the pyrolysis time is very short, mainly for the production of gas products.
Dwell time refers to the residence time of biomass raw material in the pyrolysis furnace. The length of residence time directly affects the distribution of pyrolysis products.
Longer residence time: Longer residence time favours the formation of biochar and further pyrolysis of bio-oil into gas.
Short residence time: Shorter residence time will help to bio-oil generation and reduces the chance of further pyrolysis to gas.
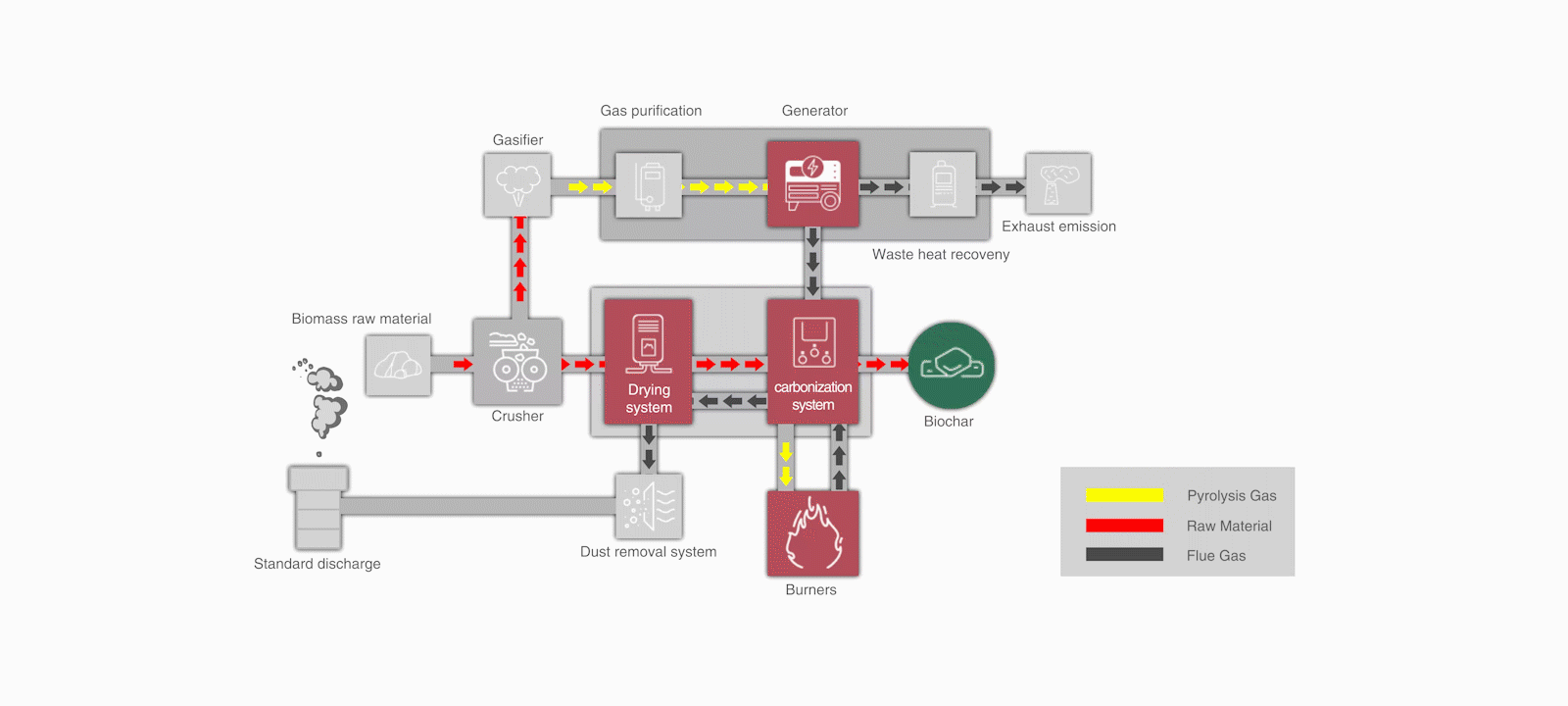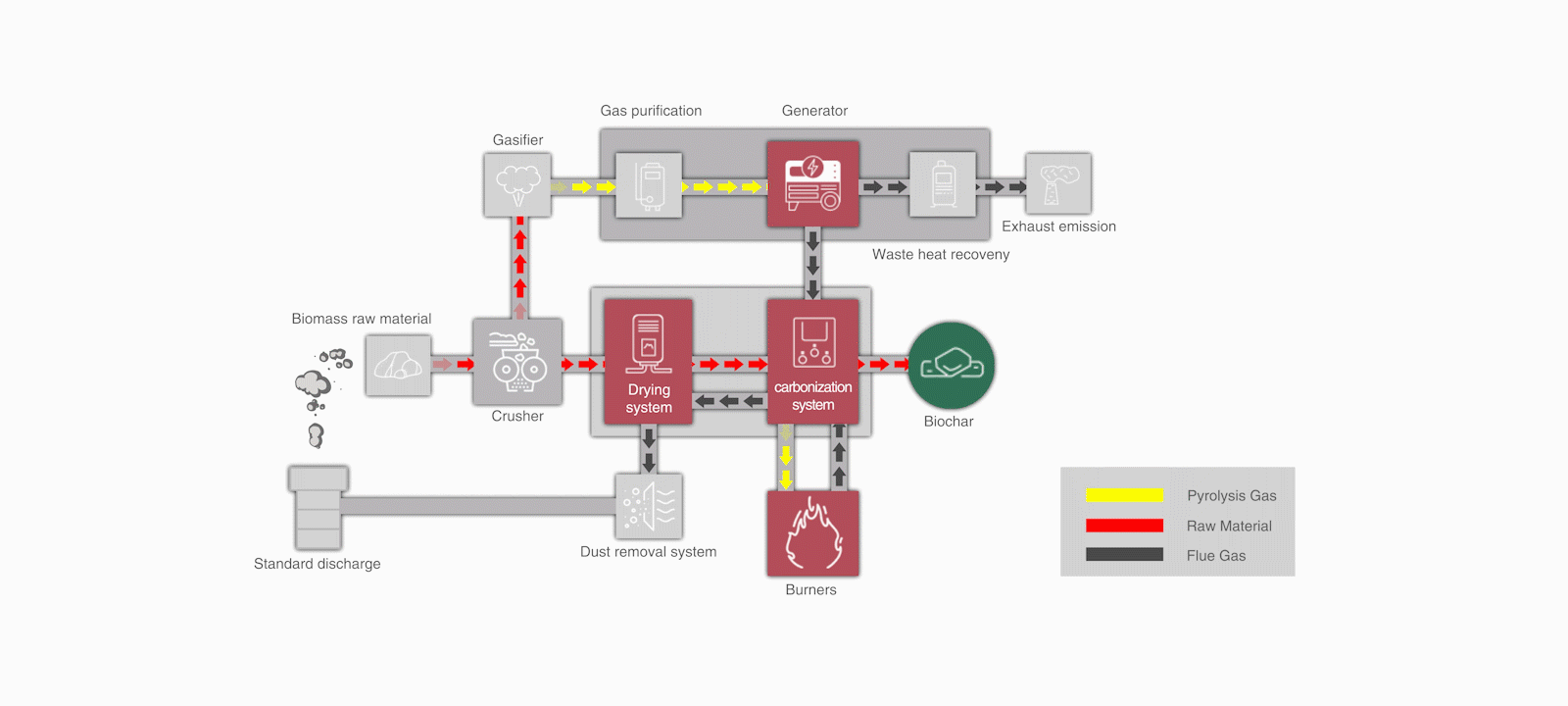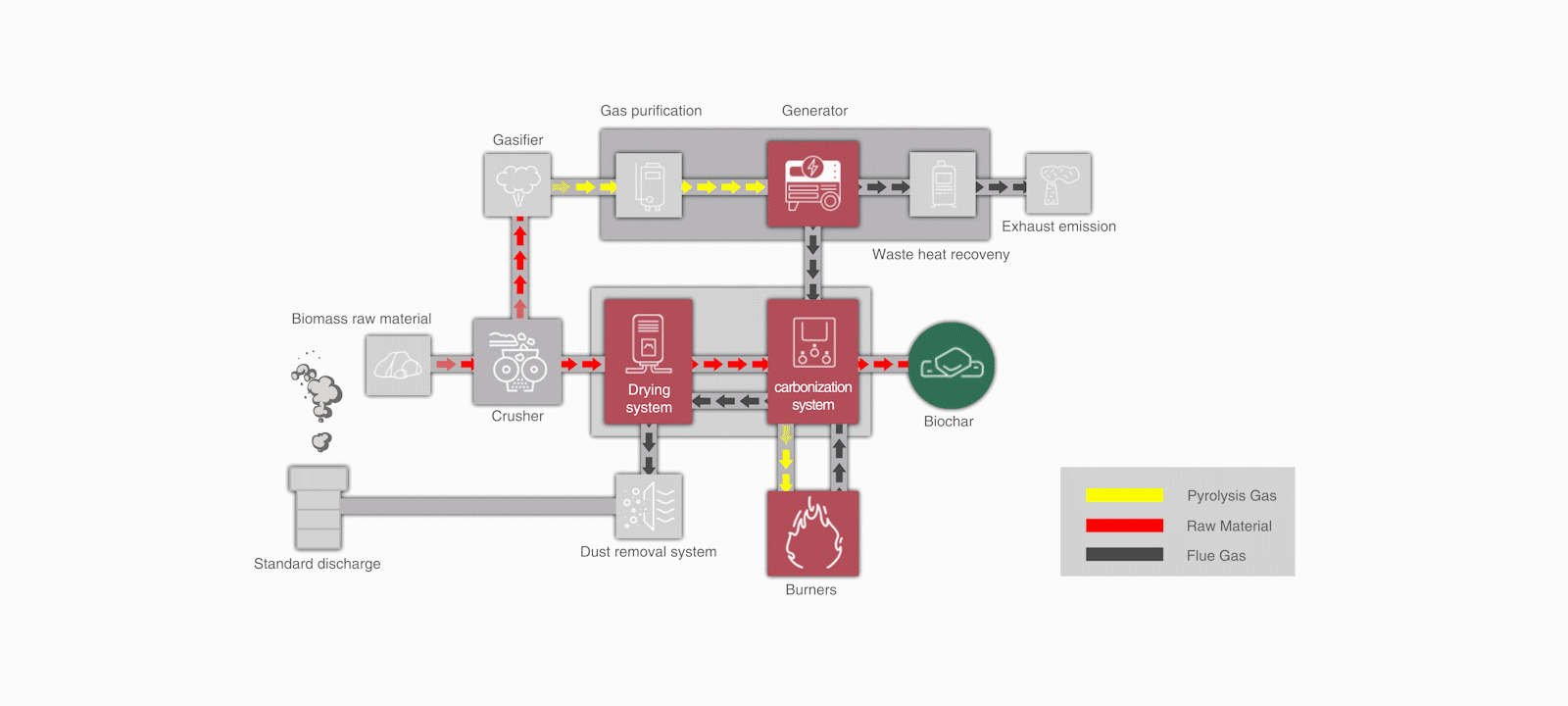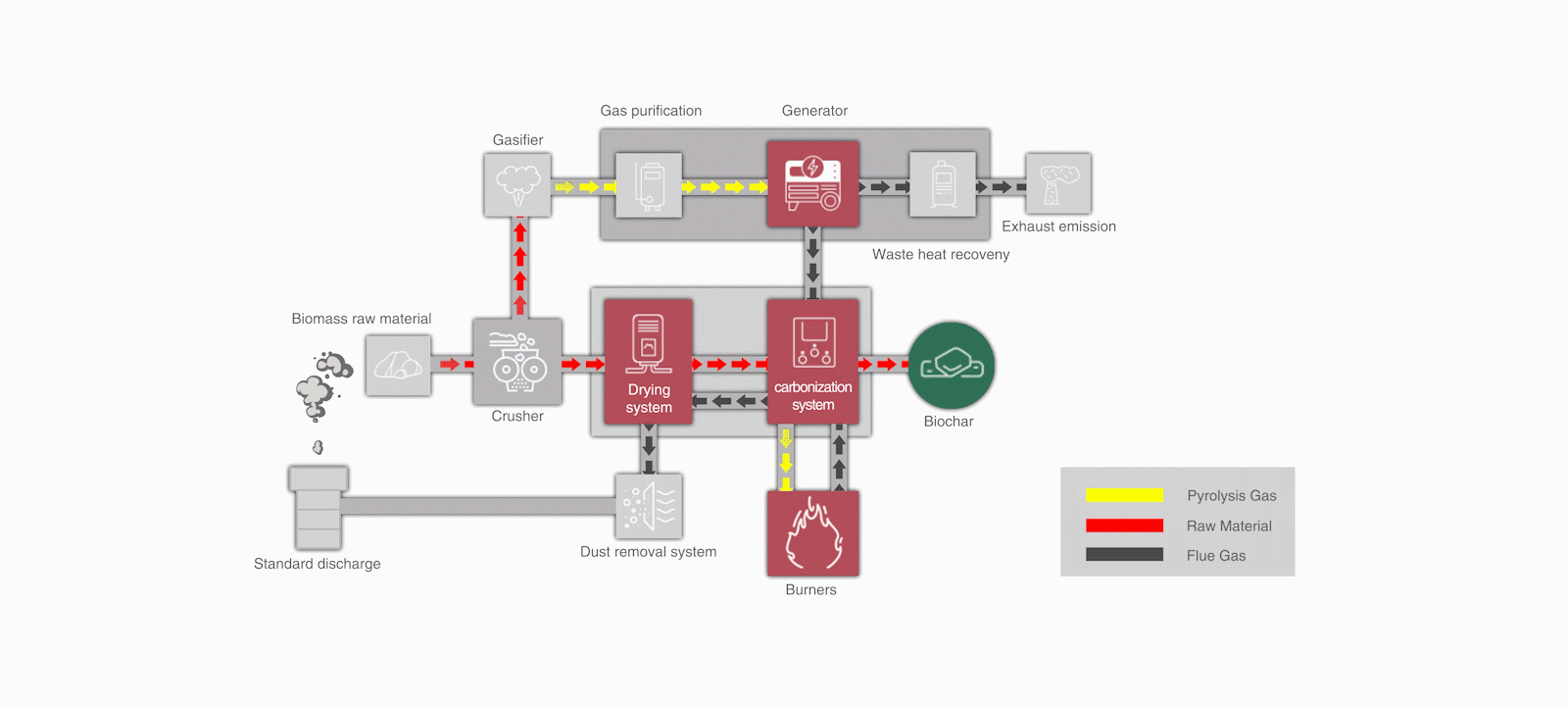
Can biochar produced through biomass pyrolysis be used for carbon trading?
Sure, but we have to clarify that the whole process of carbon sink certification is very strict. The raw materials used for biochar production, transportation, biochar production equipment, end use of the biochar, etc. must all be proven to be sustainable. Click to Check Haiqi's Puro earth Approved Biochar Machine.
.jpg)
Types of Feedstocks
There are many types of biomass feedstocks, including wood, crop residues (e.g. straw, rice husk), livestock and poultry manure, energy crops, etc. Different types of biomass feedstocks differ in their chemical composition and pyrolysis properties, and therefore their final products will also differ.
Three main products are produced through biomass pyrolysis: bio-oil, bio-char and syngas. The proportion of output of these products depends largely on the composition of the biomass. For example, feedstocks with higher lignin content are more likely to produce biochar during the pyrolysis process, while feedstocks with higher cellulose and hemicellulose content are more likely to produce bio-oil and gas.
Temperature of Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis temperature is one of the key factors affecting the distribution of biomass pyrolysis products. Generally speaking, as the pyrolysis temperature increases, the production of biochar gradually decreases, while the production of bio-oil and gas gradually increases.Low-temperature Pyrolysis : It mainly produces biochar, with less bio-oil and gas production.
Medium Temperature Pyrolysis: Bio-oil and gas production increases significantly, but biochar production remains high.
High-temperature Pyrolysis: Biochar production decreases further and bio-oil and gas production reaches a high level. Among them, high-temperature flash pyrolysis is mainly dominated by gas products.

(Haiqi CNBC Pyrolysis Waste Heat Drying Equipment)
Heating Rate of Pyrolysis
Heating speed is also an important factor affecting the distribution of biomass pyrolysis products. The faster the heating speed, the shorter the residence time of biomass feedstock in the pyrolysis process, which is conducive to generating more liquid products (bio-oil) and gas products.Slow pyrolysis: Slower heating rates allow longer pyrolysis reaction times, mainly for biochar production.
Fast pyrolysis: Conversely, the faster the heating rate, the shorter the reaction time for pyrolysis, mainly used for bio-oil production and gas product production.
Flash pyrolysis: With extremely fast heating rates, the pyrolysis time is very short, mainly for the production of gas products.
Residence Time of Feedstock in the Pyrolysis Furnace
Dwell time refers to the residence time of biomass raw material in the pyrolysis furnace. The length of residence time directly affects the distribution of pyrolysis products.
Longer residence time: Longer residence time favours the formation of biochar and further pyrolysis of bio-oil into gas.
Short residence time: Shorter residence time will help to bio-oil generation and reduces the chance of further pyrolysis to gas.

FAQ
Can biochar produced through biomass pyrolysis be used for carbon trading?
Sure, but we have to clarify that the whole process of carbon sink certification is very strict. The raw materials used for biochar production, transportation, biochar production equipment, end use of the biochar, etc. must all be proven to be sustainable. Click to Check Haiqi's Puro earth Approved Biochar Machine.
Prev Article:
2024-07-16





