Biomass Energy Plant
With the growing global demand for clean energy, biomass has gained widespread attention as a renewable energy solution and has projects deployed around the world. By converting organic waste into electricity, heat and biofuels, biomass provides an efficient energy pathway for industrial production and residential use. This reduces dependence on fossil fuels, cuts greenhouse gas emissions and turns waste into value.
What is Biomass?
Biomass is a collective term for biomass that is obtained from animals, plants, organic waste and renewable organic substances. It includes plant residues from agriculture and forestry, as well as animal manure and biodegradable industrial by-products. Unlike fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, biomass regenerates relatively quickly and can be produced sustainably if managed properly.Biomass absorbs carbon dioxide as it grows and releases it when it decomposes or is burned, so it is considered carbon neutral as long as it is sourced and processed responsibly. This makes biomass an important component of a global strategy to achieve net-zero emissions.
.png)
Types of Biomass Feedstocks
Woody Biomass
Woody biomass is woody material collected from forests or the wood processing industry. It is one of the most abundant and energy-dense forms of biomass, including:- Forestry residues, such as dead trees, logging residues, branches and stumps.
- Sawmill by-products, such as sawdust, bark and wood chips from the lumber and furniture industries.
- Non-recyclable post-consumer wood that is no longer used for furniture or construction
Agricultural Waste
Farms and agro-processing plants produce large amounts of organic waste that can be converted to energy. These wastes include:- Crop wastes such as wheat straw, rice hulls, corn stover and bagasse.
- Fruit and nut shells, including coconut shells and palm kernel shells.
- Fibrous plant matter, such as palm silk and cotton stalks.
Animal Manure and Organic Waste
Organic waste from livestock farms, food processing plants and households can be used as raw materials for biogas production. Examples include manure from cattle, poultry and pigs, municipal sludge and urban organic waste. Converting these types of biomass into electricity and other energy sources not only produces energy, but also reduces methane and carbon dioxide emissions from decomposition and takes pressure off landfills.Biomass Energy Conversion Technologies
Converting virgin biomass into usable energy requires advanced technologies. The most commonly used biomass conversion methods are:Direct Combustion
Direct combustion involves burning biomass in a boiler to produce steam, which then drives a steam turbine to generate electricity. This is the most direct and proven method of producing biomass energy. The system is usually equipped with flue gas cleaning devices to reduce emissions.
Biomass Gasification
Gasification converts biomass into a combustible gas mixture known as syngas, consisting mainly of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane. The process takes place at high temperatures and with limited oxygen, causing partial oxidation of the biomass. Syngas can be used in internal combustion engines, steam turbines and even as a feedstock for the production of liquid biofuels or chemicals.Biomass Pyrolysis Carbonization
Pyrolysis is the heating of biomass under oxygen-free conditions to break it down into three main products: biochar, bio-oil and syngas. Biochar is rich in carbon and can be used as a soil conditioner or for trading carbon credits. Bio-oil can be refined into renewable diesel, while syngas can be used to generate electricity or heat. Biomass pyrolysis carbonization is suitable for projects that require both biochar production and cogeneration. It is an ideal choice for high-quality carbon removal projects with both environmental benefits and economic value.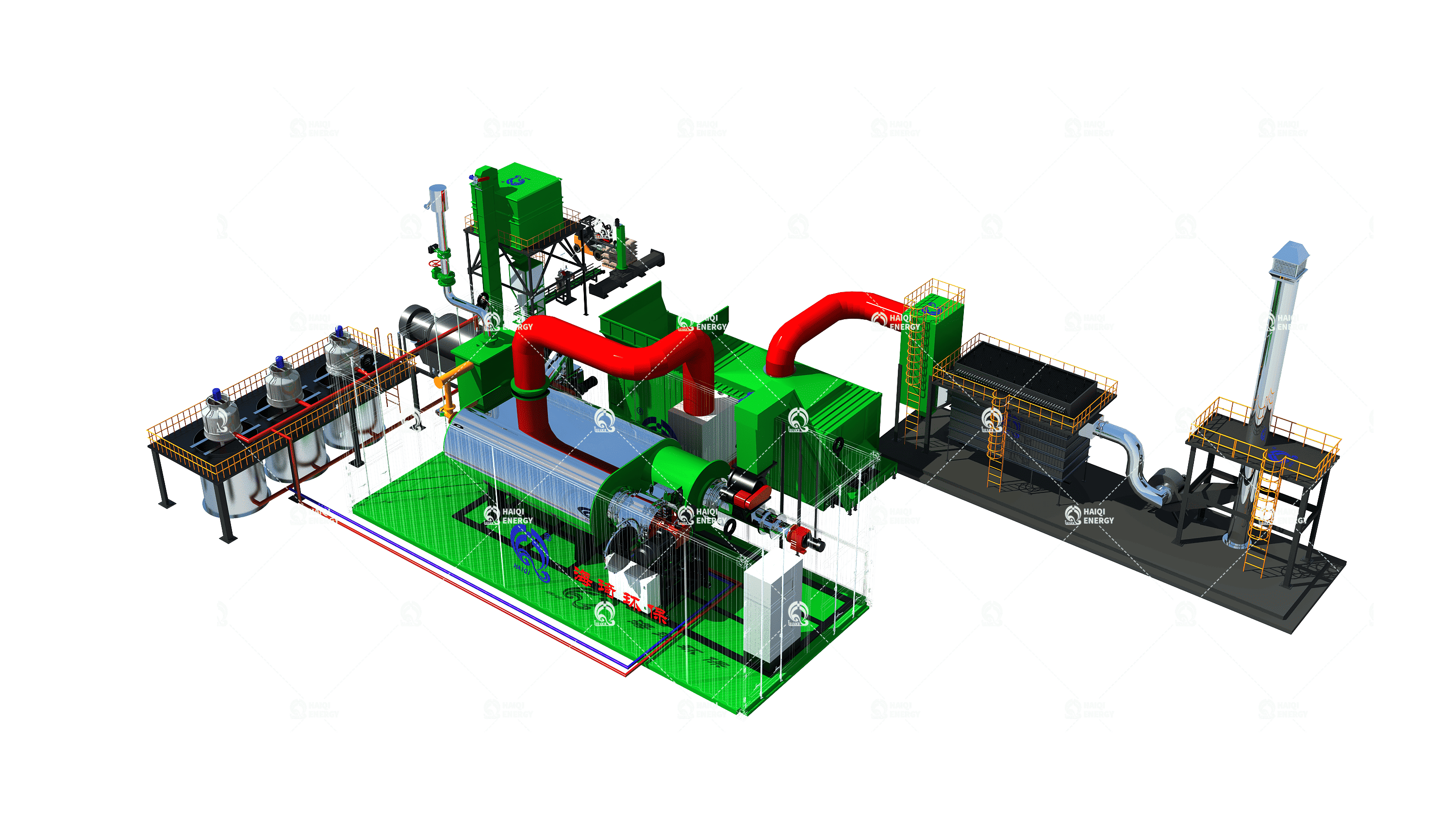
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process in which microorganisms break down organic matter in an anaerobic environment. This produces biogas (mainly methane and carbon dioxide), which can be burned to produce heat and electricity. The remaining digestate, called digestate, is rich in nutrients and can be used as fertiliser.How Does a Biomass Gasification Power Plant Work?
A biomass gasification power plant is a specialised facility that converts solid organic matter into syngas (a clean, combustible fuel mixture consisting mainly of hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane). Unlike direct combustion, gasification is a thermochemical process that offers greater efficiency and flexibility in energy applications such as power and heat generation.Raw Material Collection and Preparation
The process begins with the procurement of suitable biomass materials, typically wood chips, agricultural waste, nut shells, or other dry organic matter. After collection, the raw materials undergo pretreatment—which typically includes drying (to reduce moisture content), grinding (e.g., chipping or shredding), and sometimes pelletisation—to ensure a uniform, high-energy-density feedstock for stable gasification performance.Gasification Plant Operation
The prepared biomass is then fed into the gasifier, a high-temperature, oxygen-limited chamber. Unlike complete combustion, gasification occurs in a controlled environment where oxygen is insufficient for complete combustion. During this process, the biomass undergoes thermochemical reactions to produce combustible gases, primarily consisting of CO, H₂, CH₄, and small amounts of CO₂ and tar.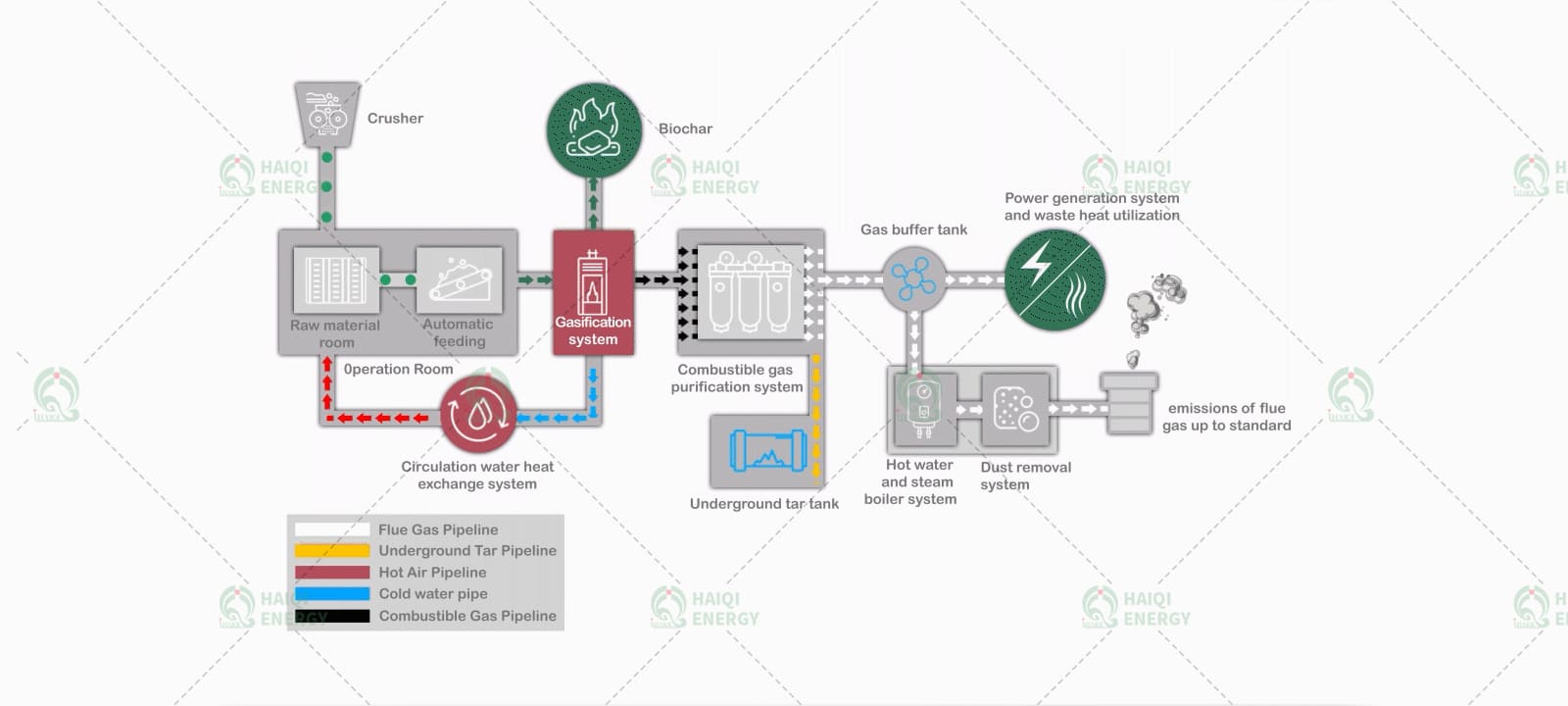
Syngas Purification and Conditioning
Before use, the raw synthesis gas must be purified to remove tar, particulates, and impurities that could damage downstream equipment. The system typically includes:
- Cyclone separators to remove solid particles;
- Washers or ceramic filters to remove tar;
- Heat exchangers to cool the gas to the optimal operating temperature.
Efficient synthesis gas purification ensures stable operation of engines/turbines and compliance with emission environmental regulations.
Power Generation
After purification and cooling, synthesis gas has two primary applications:- Gas engines or internal combustion engines: Synthesis gas is burned in the engine to drive a generator for power generation.
- Turbines: In large systems, synthesis gas may be injected into turbines, which drive generators to rotate, achieving efficient power output.
Heat Recovery and Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Integration
Biomass gasification power generation systems typically include CHP units, where the waste heat from engines or turbines can be used for industrial process heat, district heating, greenhouse heating or drying systems. This integrated approach significantly improves overall energy efficiency, with efficiency typically exceeding 75% in well-designed CHP configurations.Ash and Biochar Management
During gasification, inert ash and biochar residues are produced. These residues are collected from the bottom of the gasifier and can be used as soil conditioners or fertilisers (especially biochar, which improves soil health and stores carbon) or safely disposed of if contaminated with heavy metals (depending on the feedstock source). Forest biomass has relatively low ash content, whereas non-wood biomass, such as straw and sugarcane bagasse, has higher ash content.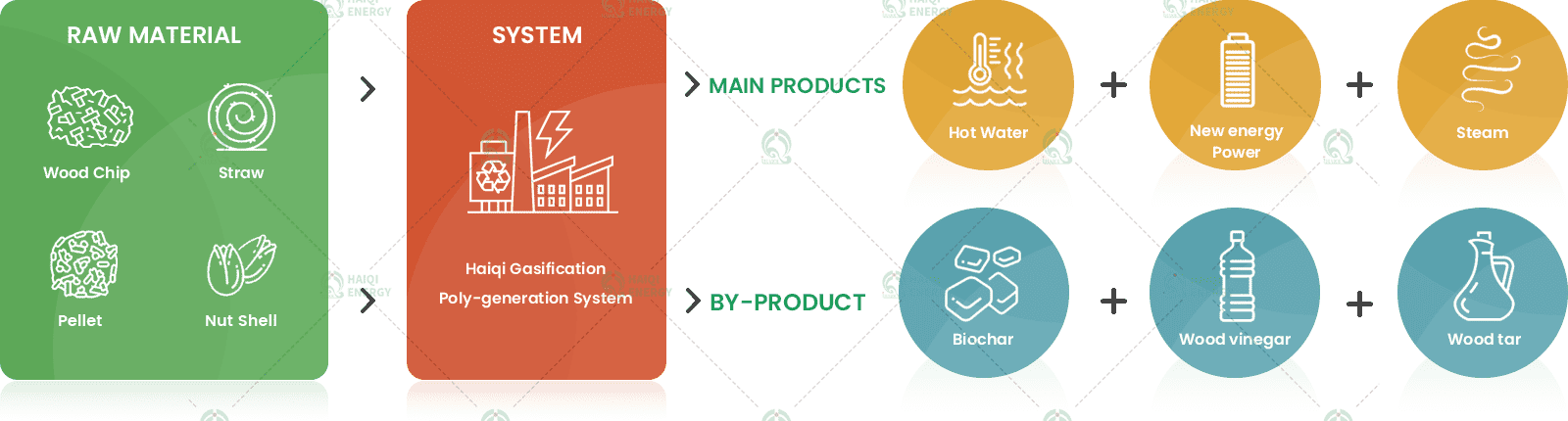
If you are seeking cleaner, more efficient energy solutions, biomass power generation plant maybe a viable option. By converting agricultural and forestry waste into green electricity, HaiQi's Biomass Gasification Plant not only helps reduce carbon emissions but also enhances resource reuse efficiency. Learn how our projects can help achieve energy self-sufficiency, reduce your factory's operating costs, and support green development goals!





