How Biochar Helps Prevent Forest Wildfires
As climate change intensifies, with the gradual deterioration of the global environment, forests are increasingly exposed to the risk of wildfires. During the summer of 2025, Europe experienced its worst year of the past two decades for wildfires in terms of area burned, and total emissions of carbon and other smoke pollutants.
Traditional forest management often generates large amounts of woody residues, branches, leaves, and other biomass — commonly referred to as slash or forestry residues. If these residues accumulate or are disposed of through open burning, they not only serve as fuel for wildfires but also contribute to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing the risks of forest fires and pollutant emissions from wildfires has become an urgent challenge for forest managers worldwide.
.png)
In this context, biochar — a highly stable carbon-rich material produced via pyrolysis of biomass under oxygen-free conditions — is receiving increasing attention. Biochar can reduce wildfire fuel loads, lower fire risk, and act as a soil amendment to improve soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability. These properties enhance forest ecosystem resilience. Additionally, by sequestering carbon in a stable form, biochar offers an effective climate mitigation tool and a potential source of carbon credits.
How Biochar Reduces Wildfire Risk
Reducing Flammable Residues and Fuel Loads
Forest operations such as thinning, harvesting, or clearing diseased trees often leave behind large amounts of low-value biomass. Traditional practices involve pile burning or open burning to reduce fire hazards. While effective in clearing fuel, these methods produce significant smoke, particulate matter, and greenhouse gas emissions, while also damaging soil and inhibiting natural regeneration.In contrast, controlled biomass pyrolysis technology to produce biochar can safely convert woody residues into stable carbon materials on-site or nearby. This approach significantly reduces flammable fuel accumulation, lowers wildfire potential, and emits fewer pollutants than open burning. By transforming potential fire hazards into stable biochar, forests are inherently safer from large-scale wildfire outbreaks.
Reducing Drought and Fire-Prone Conditions
Beyond physical fuel reduction, biochar improves soil moisture retention and microclimate regulation, indirectly reducing fire-prone conditions. Studies show that incorporating biochar into sandy or coarse-textured soils significantly enhances water-holding capacity and soil moisture stability.In drought-prone areas, improved soil water retention reduces plant stress and flammability, making vegetation less likely to ignite. Additionally, biochar can modulate soil thermal properties, reducing surface and subsurface temperature extremes and further decreasing wildfire risk.
How Biochar Improves Forest Ecology
Biochar is not just a fire prevention tool; it is also a powerful means of enhancing forest ecosystem resilience.Enhancing Soil Water Retention and Drought Resistance
Biochar's porous structure and high surface area allow it to retain water effectively when applied to forest soils. This improves water availability for plants, particularly in arid or nutrient-poor soils, enhancing their tolerance to drought and heat stress. Enhanced soil moisture can support stable forest growth, even under extreme climatic conditions.Improving Soil Fertility and Supporting Microbial Activity
Biochar improves soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. It increases cation exchange capacity (CEC), stabilizes soil pH, and reduces nutrient leaching. Its porous structure provides habitats for soil microorganisms, promoting a healthy microbial community that drives nutrient cycling.Research demonstrates that biochar amendment can improve soil enzyme activity, fungal community structure, and microbial functionality for multiple years post-application. This promotes a self-sustaining, nutrient-rich soil environment that supports forest productivity and ecological stability, reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers.
Enhancing Carbon Sequestration
Unlike decomposable organic matter such as leaves and branches, biochar is highly stable and can persist in soils for centuries. By converting biomass into biochar, carbon is effectively sequestered, reducing atmospheric CO₂ and contributing to climate mitigation. For forest managers, this means transforming low-value residues into a long-term carbon storage solution, which can also generate carbon credits under climate programs.Restoring Degraded Lands and Increasing Resilience
In forests degraded by fire, pests, over harvesting, or soil erosion, biochar can restore soil structure, improve water and nutrient retention, and promote plant regeneration. Enhanced soil conditions support seed germination and seedling growth, accelerating ecological recovery. Additionally, biochar fosters microbial diversity and ecosystem functions, strengthening forest resilience against future droughts, temperature extremes, and other environmental stresses.Applications of Biochar Production in Wildfire Prevention
Biochar is no longer just a theoretical solution; many countries, especially those frequently ravaged by wildfires such as North America and Australia, have begun to apply biochar in forest fire management and ecological restoration projects.Mobile Biochar Machine for On-Site Fuel Load Reduction
In wildfire prevention, mobile biochar systems are emerging as a highly flexible and effective solution. These units can be deployed directly in high-risk forest areas, converting accumulated fuels such as branches, bark debris, pine needles, and deadwood into stable biochar on site. Compared with traditional slash burning or long-distance biomass transport, mobile systems significantly lower fuel loads while avoiding carbon emissions and ignition risks during transportation. This enables forest management teams to process hazardous biomass efficiently on-site while generating a valuable product simultaneously.Industrial-Scale Biochar Production for Regional Wildfire Mitigation
At a larger scale, industrial biochar production systems provide long-term and stable value in regional wildfire prevention strategies. High-capacity pyrolysis facilities can continuously process low-quality forest residues—such as beetle-kill trees, post-fire standing deadwood, and thinning waste—turning them into large quantities of biochar. Such industrial-scale biochar production project not only support sustainable forest operations but also generate consistent carbon credit revenue for governments and forestry agencies.Energy-Coupled Biochar Systems for Remote Forest Operations
Integrating biochar production with renewable energy generation further enhances its strategic role in wildfire prevention. Through pyrolysis, forest residues can be converted into both biochar and renewable heat or electricity, which can power remote ranger stations, forest operation bases, off-grid communities, and emergency communication facilities. This "risk reduction — energy production — biochar creation" model transforms forest management from a cost center into a sustainable energy-and-carbon-credit system. It improves wildfire resilience while strengthening energy independence in remote forest regions.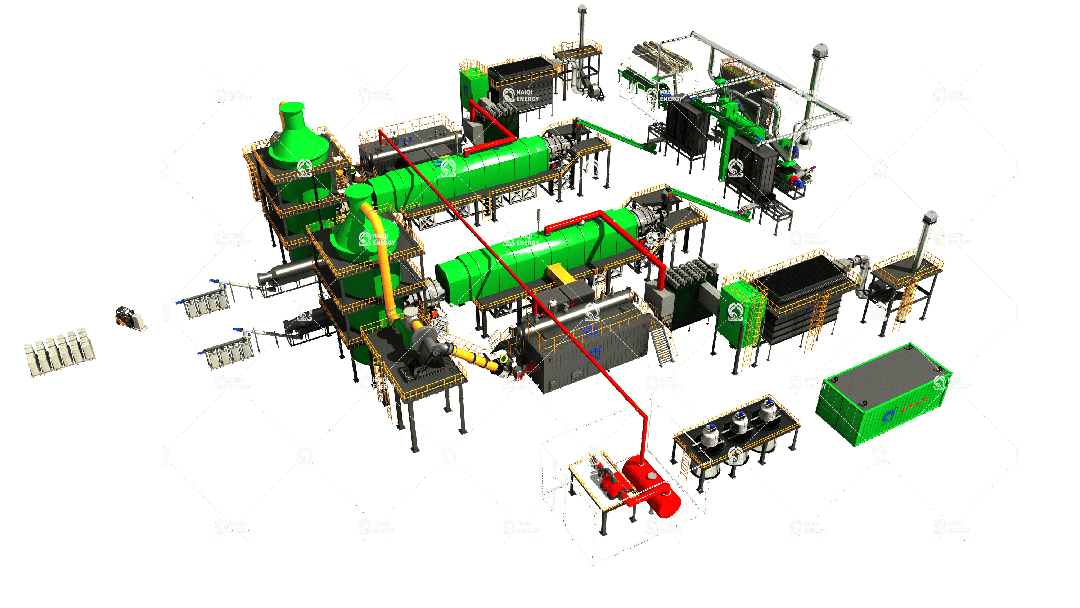
Case Study
The California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection invested nearly $800,000 in two mobile biocahr pyrolysis machines to reduce the threat of wildfires. Forestry workers collect branches and residual biomass from thinning operations and controlled burning. These residues are no longer left to burn in the open or decompose naturally; instead, they are fed into the mobile pyrolysis units to produce biochar on-site. This process not only reduces wildfire fuel but also provides a carbon-negative solution: biochar, which can be applied in areas such as carbon sequestration, agriculture, and ecosystem restoration.As pyrolysis technology matures and climate finance mechanisms support carbon sequestration, biochar will increasingly become an essential tool for forest fire management, ecological restoration, and global climate mitigation efforts. Industrial-scale biochar production, coupled with carbon credit markets and climate-smart forest management strategies, presents a sustainable and economically viable pathway for resilient landscapes.
If you’re exploring how biochar can play a role in your forest management strategy—or how it can support the sustainability goals of your organization—we'd be delighted to discuss the possibilities with you. As a technology partner of Puro earth, we are committed to developing high-quality, verifiable biochar CDR projects that meet international standards. Also, we help forestry owners, municipalities, and private companies turn waste biomass into long-term environmental and economic value as biochar project developers and investors. Curious what biochar could mean for your forest, your business, and the planet? Contact now!





